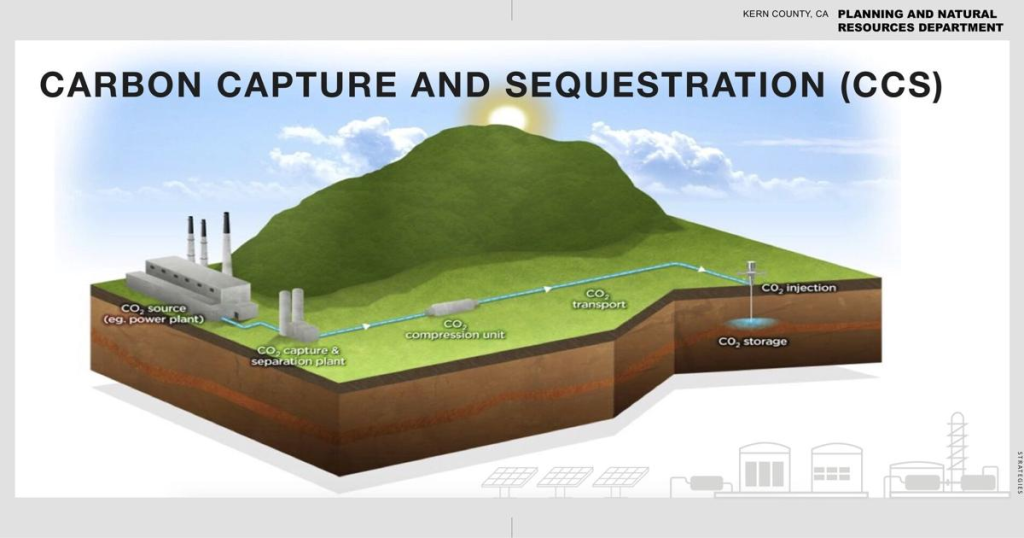
Kern County Gives Green Light to California Resources Corp.’s Carbon Terra Vault

Kern County’s Board of Supervisors has unanimously approved California’s first carbon capture and storage (CCS) project. The project, led by California Resources Corp. (CRC), will capture and store millions of tons of CO2 underground. CRC is the state’s largest oil and gas producer. The Carbon Terra Vault project aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in the San Joaquin Valley.
Project Details
- Location: Elk Hills Oil and Gas Field, south of Buttonwillow
- Storage capacity: Up to 49.1 million tons of CO2 in two underground reservoirs
- Annual capture target: 1.46 million metric tons of CO2
- Injection depth: Over one mile deep into the Monterey Formation
- Construction timeline:
- Two years for carbon capture plants
- One year for pipelines
The CO2 will be extracted from natural gas produced at the field before being burned at CRC’s power plant. This power plant supplies energy to Pacific Gas & Electric. Carbon will also be captured from a proposed hydrogen plant and a direct air capture project.
Support and Opposition
The Newsom administration has endorsed the project, viewing CCS as critical to California’s efforts to combat climate change. CRC CEO Francisco Leon emphasized the project’s potential to preserve high-paying jobs while reducing carbon emissions. He also highlighted the company’s commitment to investing in the community.

However, environmental advocates have raised concerns about potential air pollution and the safety of injecting CO2 underground. They argue that the project could prolong the life of fossil fuel industries in the area. There are also concerns about potential health risks to low-income communities in the San Joaquin Valley.
Regulatory Requirements
Before construction can begin, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) must give the project final approval. The California Air Resources Board must also certify the project’s eligibility for state clean-fuel credits. The EPA will require CRC to monitor the injection wells for a century to ensure groundwater remains uncontaminated.
California’s Carbon Capture Landscape
The Carbon Terra Vault project is part of a broader push for CCS in California. Federal officials are currently reviewing 13 other carbon capture proposals in the state. CRC, through its Carbon TerraVault subsidiary, holds seven of those applications, seeking authorization for 38 wells. These projects could qualify for federal tax credits worth nearly $6 billion over a 12-year period. The Inflation Reduction Act has made these tax credits available.
California is working towards its goal of reaching net-zero carbon emissions by 2045. State officials have acknowledged that CCS will play a more significant role than originally envisioned. This technology is expected to help reduce greenhouse gas emissions from large sources in the state.
Conclusion
The approval of the Carbon Terra Vault project marks a significant milestone in California’s efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. While the project has received support from the Newsom administration and CRC, environmental advocates have expressed concerns. As the project moves forward, it will be important to address these concerns and ensure that the project meets all regulatory requirements. The success of this project could pave the way for more CCS projects in California and beyond.
Read More: Hydrogen Car Fueled by Sewage Aims to Break Speed Record