The UK’s carbon capture and storage (CCS) sector is entering a crucial phase with major projects moving from planning to construction in 2025. This development marks significant opportunities for civil engineering firms, with investments potentially reaching £30 billion by 2030.
Key Carbon Capture Projects Reaching Financial Close
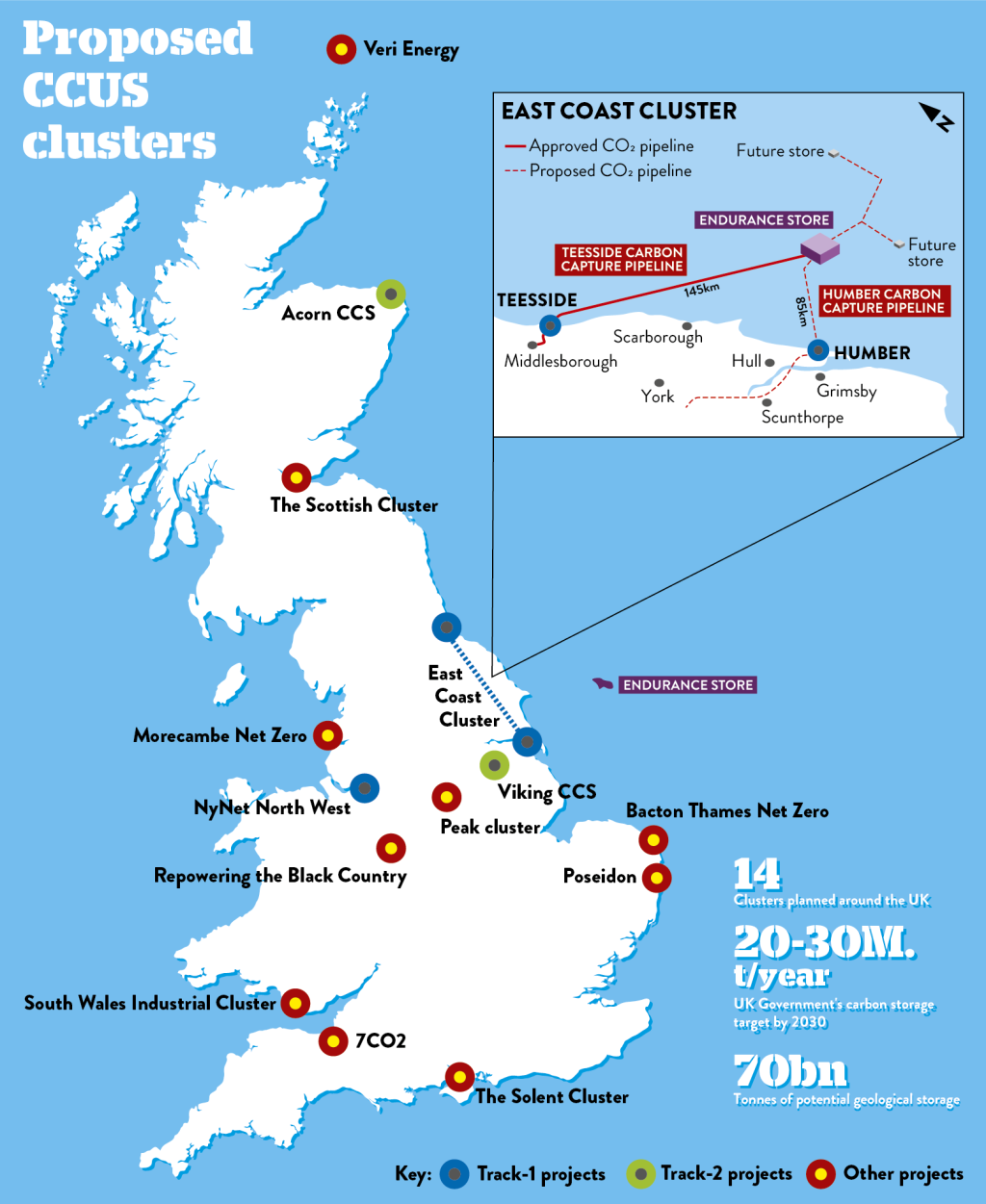
The East Coast Cluster has achieved several major milestones:
- Northern Endurance Partnership infrastructure:
- 145km offshore pipeline network
- Carbon dioxide transport system
- Connection to multiple industrial facilities
- Storage in Endurance saline aquifer at 1000m depth
- Net Zero Teesside Power development:
- New gas-fired power station construction
- Integrated carbon capture technology
- First commercial-scale power CCS project in UK
- Financial close achieved December 10, 2025
These developments represent the first major implementation phase of the UK’s carbon capture strategy, setting precedents for future projects.
Investment Scale and Civil Engineering Opportunities
The carbon capture sector presents substantial opportunities for civil engineering firms. Private sector investment is expected to reach between £20-30 billion by 2030, supported by a significant government funding commitment of £21.7 billion over 25 years. Based on Spirit Energy’s Peak Cluster model, approximately 20% of infrastructure costs will be allocated to civil engineering works.

Project Components Requiring Civil Engineering Expertise
- Construction of carbon capture facilities at power plants
- Pipeline infrastructure (onshore and offshore)
- Storage facility development
- Industrial plant retrofitting
- Cooling and absorption tower construction
Carbon Storage Targets and Infrastructure Requirements
The UK government has established ambitious carbon storage targets for the coming decades. By 2030, the country aims to store 20-30 million tonnes of carbon annually, increasing to 50-60 million tonnes by 2035. The British Geological Survey has identified over 70 billion tonnes of potential geological storage capacity across the UK, providing ample opportunity for long-term development.
Current Project Status and Development
The UK’s cluster-based approach to carbon capture development has seen significant progress. The Track-1 clusters, comprising the East Coast Cluster and HyNet Cluster in Northwest England and North Wales, have received approval and are moving forward. Track-2 clusters, including Acorn in Scotland and Viking in Teesside, are currently in development phases, representing the next wave of carbon capture infrastructure.
Technical and Economic Considerations

Cost Factors and Infrastructure Impact
Current carbon storage costs range from £100-200 per tonne, significantly higher than the UK Emissions Trading Scheme price of £41.84 per tonne as of January 2025. Infrastructure requirements are substantial, with power plant installations typically requiring double the existing facility footprint. These factors present both challenges and opportunities for civil engineering innovation.
Industry Challenges and Solutions
The carbon capture industry faces several significant challenges that require innovative engineering solutions. Energy requirements for carbon extraction remain a primary concern, alongside complex infrastructure coordination needs. Space constraints for retrofitting existing facilities demand creative engineering approaches, while the increasing demand for skilled construction workforce requires strategic workforce development.
Future Development and Industry Impact
The Carbon Capture and Storage Association’s identification of 90 potential projects across the UK represents a transformative opportunity for the civil engineering sector. These developments could establish an annual carbon storage capacity exceeding 90 million tonnes. The cement industry, in particular, stands to benefit significantly, with CCS technology potentially enabling a 60% reduction in emissions by 2050.
Project Implementation and Timeline Management

Success in carbon capture infrastructure development depends on meticulous timeline management and project coordination. The development of the Peak Cluster demonstrates this complexity, with plans for 180km of onshore and 75km of offshore pipelines. This infrastructure must be carefully integrated with existing industrial facilities while maintaining operational efficiency.
Investment and Regulatory Framework
Investment strategies and regulatory frameworks play crucial roles in project development success. Government allocation processes and funding mechanisms must provide clear pathways for project advancement. Risk management strategies are evolving as the industry matures, with construction cost optimization becoming increasingly important as more projects move from planning to implementation.
Industry Growth and Future Prospects
Industry growth hinges on successful implementation of pioneering projects like the East Coast Cluster. These early initiatives will establish cost-effective delivery models and best practices for future developments. The sector’s expansion presents significant opportunities for civil engineering firms to develop expertise in this emerging field.
Did You Know? HySE: Japanese Alliance Advances Hydrogen Engine Technology













